FAFSA is one of those things that everyone has heard of, but no one really understands. You know you have to fill it out every year and you know it determines how much financial aid you or your kid(s) get for college, but that’s about it. Does having a 529 Plan affect financial aid? How exactly is it calculated anyway? We’re about to pull the mask off and see what FAFSA really is, and forewarning – there are some calculations.
What is FAFSA?
FAFSA is the Free Application for Federal Student Aid. Students are required to fill out a FAFSA form to be eligible for federal grants, loans, and work-study. Many states and colleges use FAFSA information to determine eligibility for school and state aid, and some private lenders may also use FAFSA to determine eligibility for loans. So almost everyone who attends college needs to fill out a FAFSA.
When can I submit FAFSA?
The application becomes available on October 1st every year. For students attending college between July 1, 2020 and June 30, 2021 the window for filing is October 1, 2019 to June 30, 2021.
The generous time frame for filing means you can file any time you or your child are attending college; however the earlier you file, the more grant money you’re likely to receive. State and college deadlines for FAFSA may be different than the federal deadline, so it’s best to file as early as you can every year.
What do I need to submit FAFSA?
To complete the application, you will need to provide:
- Your social security number (or alien registration number if not a citizen)
- Federal income tax returns and W-2s (may be able to use IRS Data Retrieval Tool to transfer data automatically)
- Bank statements and records of investments
- Records of untaxed income
- An FSA ID to electronically sign the application
For dependent students, the information must be provided for parent(s) as well.
How is my aid calculated?
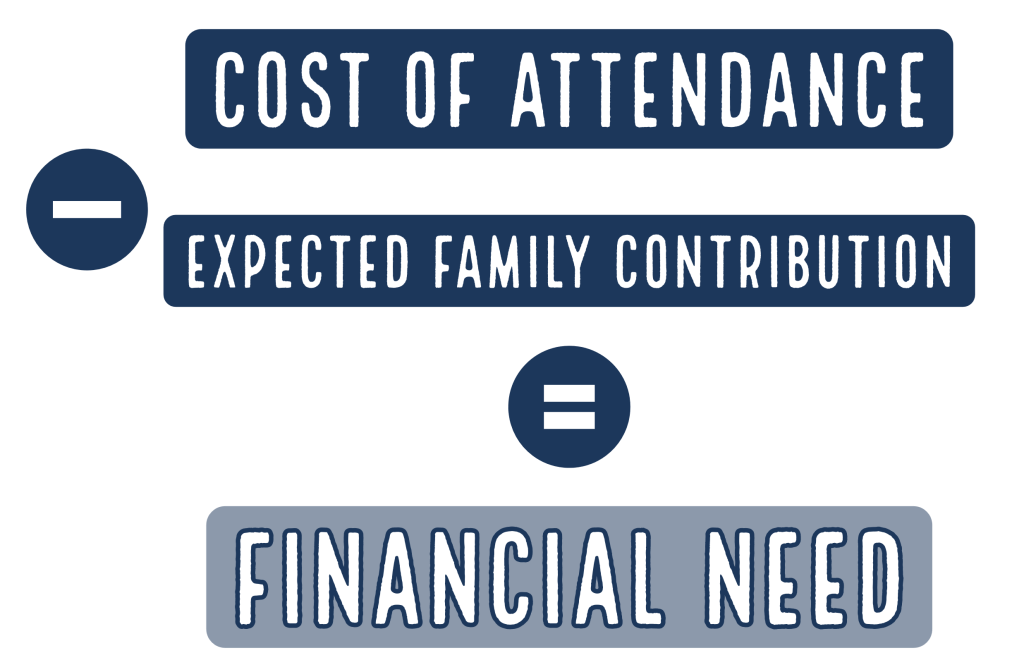
The formula for determining the amount of need-based financial aid a student is eligible for is Cost of Attendance (COA) – Expected Family Contribution (EFC) = Financial Need.
What are the different types of need-based financial aid?
Need-based financial aid includes the following:
- Federal Pell Grants
- Direct Subsidized Loans
- Federal Perkins Loans
- Federal Work-Study
- Federal Supplemental Educational Opportunity Grant (FSEOG)
What is EFC (Expected Family Contribution) and how is it calculated?
Expected family contribution is not understood well by many FAFSA applicants and is the most mysterious component in the financial aid formula. EFC helps determine how much need-based financial aid you can receive, or if you receive aid at all.
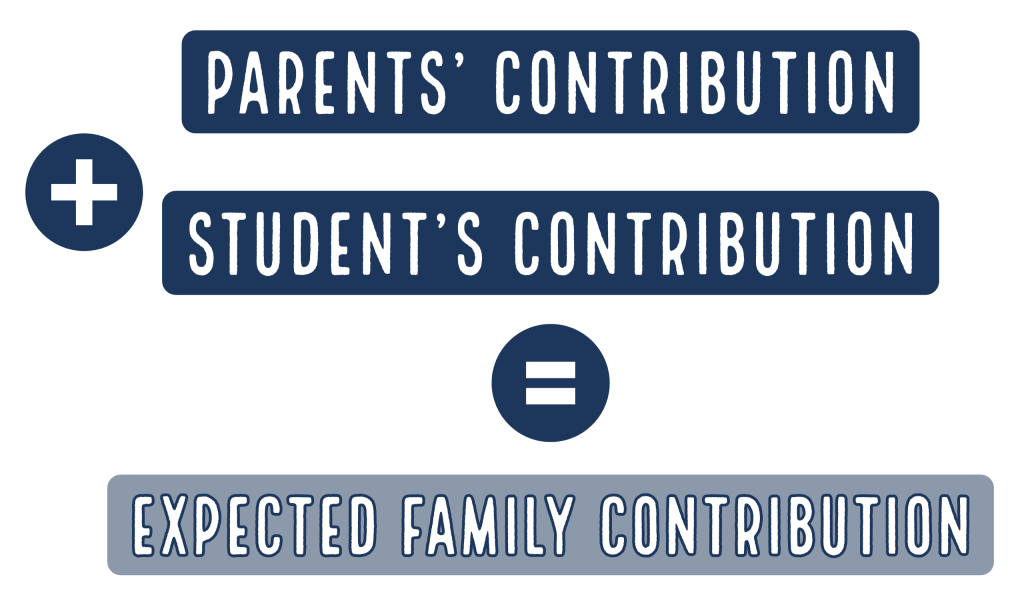
For dependent students, the expected family contribution is how much the student and parent(s) are expected to be able to contribute towards college costs. The Department of Education releases a detailed breakdown of the EFC formula every year*. The simple formula to determine the parents’ contribution is Available Income (AI) + Contribution from Assets = Adjusted Available Income (AAI). AAI ÷ Number of children in college = Parents’ Contribution.
*Information provided is based on the 2018-19 EFC formula. The formula may change from year to year, so please check with the Department of Education for any changes or updates.

The simple formula for calculating the student’s contribution is Available Income + Contribution from Assets = Student’s Contribution. Then, just add up the student’s contribution and parents’ contribution and you get the EFC.
How is available income determined?
Parents’ total income includes taxable income, untaxed income, and benefits. If the parents’ taxable income is less than $25,000, and they meet one of three minor conditions (filed taxes, eligible to file taxes, or not required to file taxes, etc.) the EFC is automatically $0.
Allowances against parents’ income include federal income tax paid, state and other taxes, Social Security tax allowance, income protection allowance, and employment expense allowance. Total Income – Total Allowances = Available Income (AI).
The student’s total income includes taxable income, untaxed income, and benefits. The student allowances include federal income tax paid, state and other taxes, Social Security tax allowance, income protection allowance, and allowance for parents’ negative AGI. Total Income – Total Allowances = Available Income (AI).
What assets are included in the contribution from assets calculation?
Assets included in calculating the parents’ contribution from assets are as follows:
- Cash, checking, and savings accounts
- Net worth of investments* (including 529 plans)**
- Adjusted net worth of business/farm
The formula for determining parents’ contribution from assets is Discretionary Net Worth × 0.12 = Contribution from Assets,where Discretionary Net Worth = Included Assets – Education Savings and Asset Protection Allowance.

*Investments include but are not limited to real estate (except primary residence), trust funds, mutual funds, CDs, stocks, bonds, commodities, etc. 529 plans and Coverdell savings accounts are included in investments. Life insurance, pension funds, annuities, non-education IRAs are not counted as investments.
**Parents have an allowance for education savings and asset protection based on age, and for 2018-2019 the allowance ranged from $0 to $33,600. For parents between 40-50, the allowance ranged from $17,700 to $22,300 for two parents.
The student’s contribution from assets is determined using the same formula, with a few minor differences:
- The student can not take an education savings and asset protection allowance and
- The asset conversion multiplier is 0.20 instead of 0.12.
Other factors that affect need-based financial aid
Enrollment status, maintaining satisfactory academic progress, and year in school also affect need-based financial aid. Students must be enrolled or accepted in in an eligible degree or certificate program, and for direct loans students must be enrolled at least half-time. Other conditions may apply in different states or at different colleges.
Knowing exactly how FAFSA is calculated, what documents you need, and when deadlines are should make it a little less scary. Now you might even be looking forward to getting Junior out of the house. For even more great college tips, check out our video on the best ways to save and pay for college.
Want to learn more about the dos and don’ts of saving for college? Watch our full episode, The Best Ways to Save and Pay for College.